Macao can learn how to develop through innovation from Shenzhen’s experience of its 40-year reform and opening-up, and play a unique role in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) and the national development, said a Macao scholar Ip Kuai Peng in a recent interview with Xinhua.
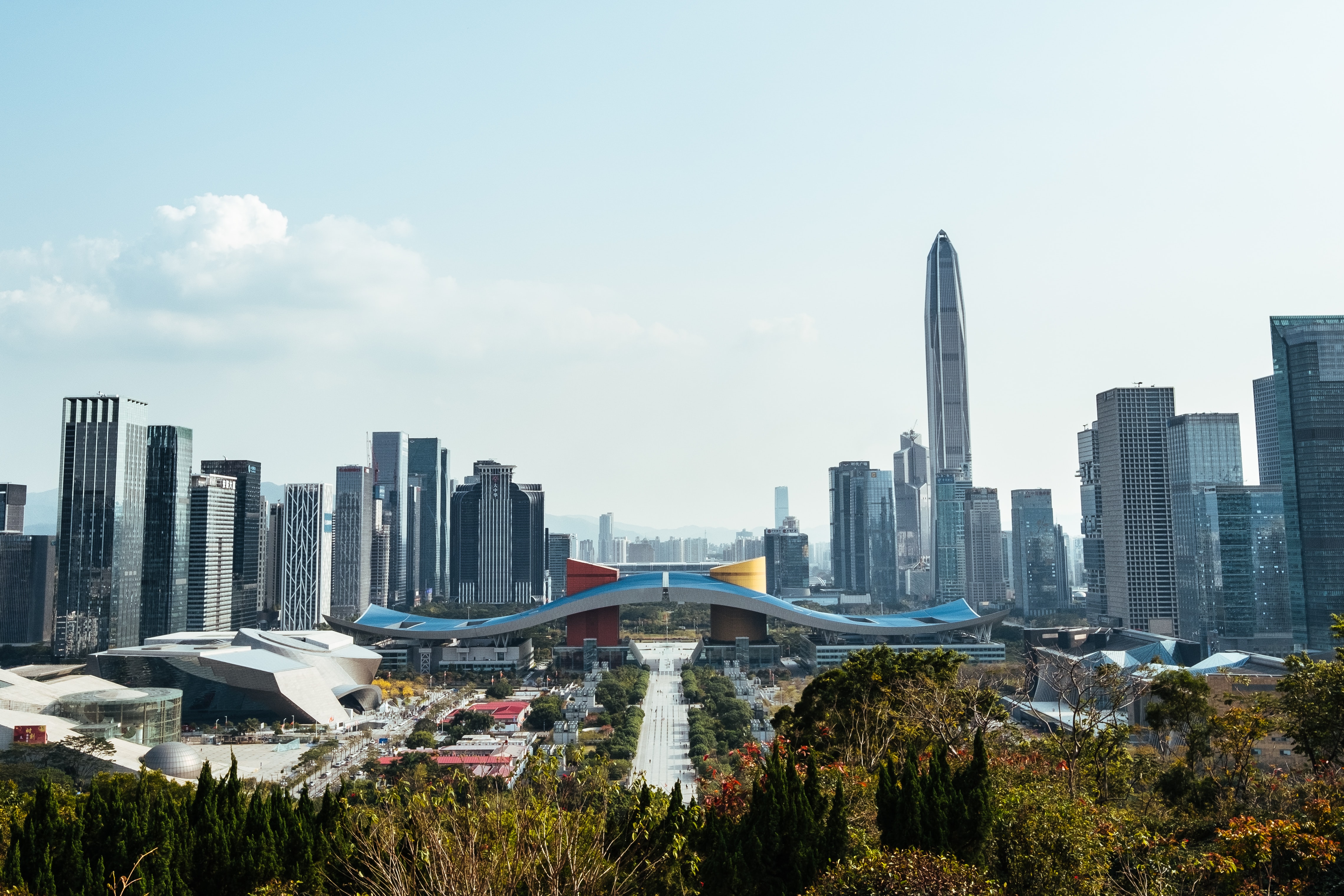
Ip, the pro-rector of City University of Macau and the director of Research Center for Macao Social and Economic Development, said Shenzhen Special Economic Zone (SEZ) has become an important engine of GBA from a small fishing village in 40 years, which is undoubtedly a successful model of reform and opening up.
He believed that the key to Shenzhen’s success is to emancipate the mind and take a series of forward-looking and pragmatic reforms. Such reforms has empowered scientific and technological innovations to be the engine of economic development.
Ip mentioned that Shenzhen has improved urban governance systems and capabilities, and built a market environment, a policy environment, and a public service system that are conducive to innovation, and promoted the free flow of talents, capital, information, technology and other factors in a virtuous circle.
“Shenzhen’s experience also provides valuable experience for Macao to promote moderate economic diversification and realize sustainable development,” he said.
In order to realize sustainable and healthy development, Macao should create a policy and an institutional environment both conducive to innovation, strengthen cooperation with GBA cities to expand Macao’s space of development, he added.
He suggested that Macao can also use its advantages to cooperate with Shenzhen.
For example, Macao can make use of its resources as a service platform for business cooperation between China and Portuguese speaking countries (PSCs) and play its role as a window and a bridge to facilitate Shenzhen’s economic and trade cooperation with PSCs, and help Shenzhen enterprises explore PSCs markets.
Shenzhen has comprehensive modern industrial systems with a large number of iconic innovative enterprises, state key laboratories and a cluster of university resources, he said.
Both sides can strengthen cooperation in scientific and technological innovation, such as the Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong-Macao Science and Technology Innovation Corridor.
In recent years, Macao has had some emerging industries such as finance, exhibition, and cultural creativity. It has been designated as a Creative City of Gastronomy by UNESCO and striven to become a world tourism and leisure centre.
Ip said Macao can match Shenzhen’s advantages in financial services, e-commerce, and high-end tourism industry. For example, Macao can cooperate with Shezhen’s Qianhai financial reform pilot zone, in fields such as renminbi clearing and finance lease.
Talking about Zhuhai, which is Macao’s close neighbour city and also a SEZ, he said the cooperation between Macao and Zhuhai can also learn from Shenzhen’s experience.
China has recently unveiled a list of 40 authorized measures to facilitate the pilot reforms in Shenzhen. Such innovation can inspire the development of Hengqin Guangdong-Macao Deep Cooperation Zone between Macao and Zhuhai, he added.
He suggested that Macao and Zhuhai can promote institutional innovation in civil and commercial laws, trade and tax regulations, explore policy coordination and planning convergence in fields of science and technology, finance, business and social welfare.
In such way, the factors of talent, capital and technology can flow conveniently in Hengqin between Guangdong and Macao with high efficiency. The advantages and resources of Guangdong and Macao can be optimized and forged into a good example of collaborative innovation development of GBA, he added.
(China Daily)
PHOTO © Robert Bye