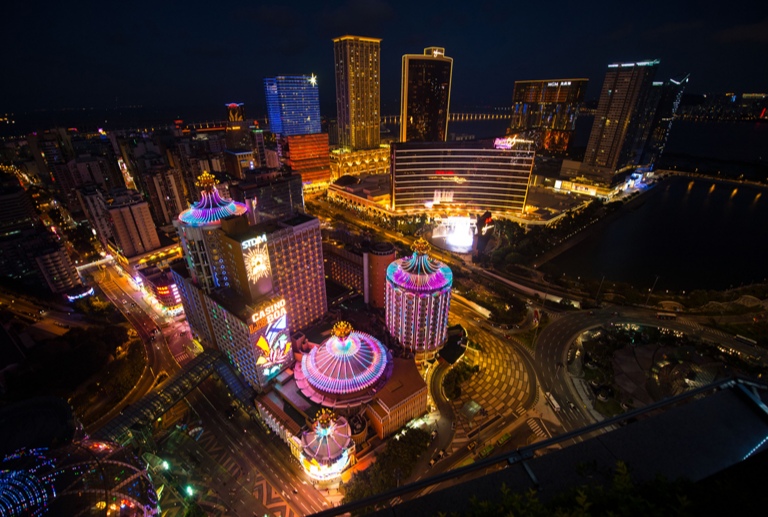
Nearly 15 per cent of Macau’s employees worked for the gaming sector in the second quarter of the year, according to data released by the Statistics and Census Bureau (DSEC) on Thursday.
According to a DSEC statement, the number of full-time employees in the gaming sector rose by 2.8 per cent year-on-year to 57,840 in the second quarter, accounting for 14.9.4 per cent of Macau’s total employment of 387,200 at that time.
Female employees made up 57.5 per cent of the gaming industry workforce in the April-June period. Shift workers accounted for 94.89 per cent of the total number of employees in the sector.
Full-time employees’ average earnings – excluding bonuses – in June grew by 3.8 per cent year-on-year to 24,550 patacas. Resident and non-resident employees earned an average of 24,680 patacas and 22,120 patacas respectively.
The number of dealers (croupiers) increased by 4.8 per cent to 25,213 in the second quarter. Females accounted for 67.4 per cent of the total number of dealers. Some 43.6 per cent of all full-time gaming sector full-time employees were dealers, whose average earnings rose by 2 per cent year-on-year to 20,850 in June.
Females accounted for 56.9 per cent of the sector’s total number of full-time employees. While females’ average earnings amounted to 23,570 patacas in the second quarter, males’ stood at 25,870 patacas, 9.7 per cent more than their female counterparts.
Job vacancies increased by 81 year-on-year to 904 in the second quarter, including 588 vacancies for dealers.
In the second quarter, the sector employed 3,129 directors and managers, a year-on-year increase of 18.1 per cent. Males accounted for 57.6 per cent of all directors and managers.
While the average earnings of non-resident directors and managers rose by 8.9 per cent year-on-year to 81,360 patacas in June, those of their local counterparts increased by 2.3 to 50,700 patacas
In the second quarter, 1,942 new employees were hired, up by 48.1 per cent year-on-year. According to the Macau Post Daily, the requirement for knowledge of Mandarin and English accounted for 77.2 per cent and 21.9 per cent of the total number of vacancies’ recruitment prerequisites respectively.