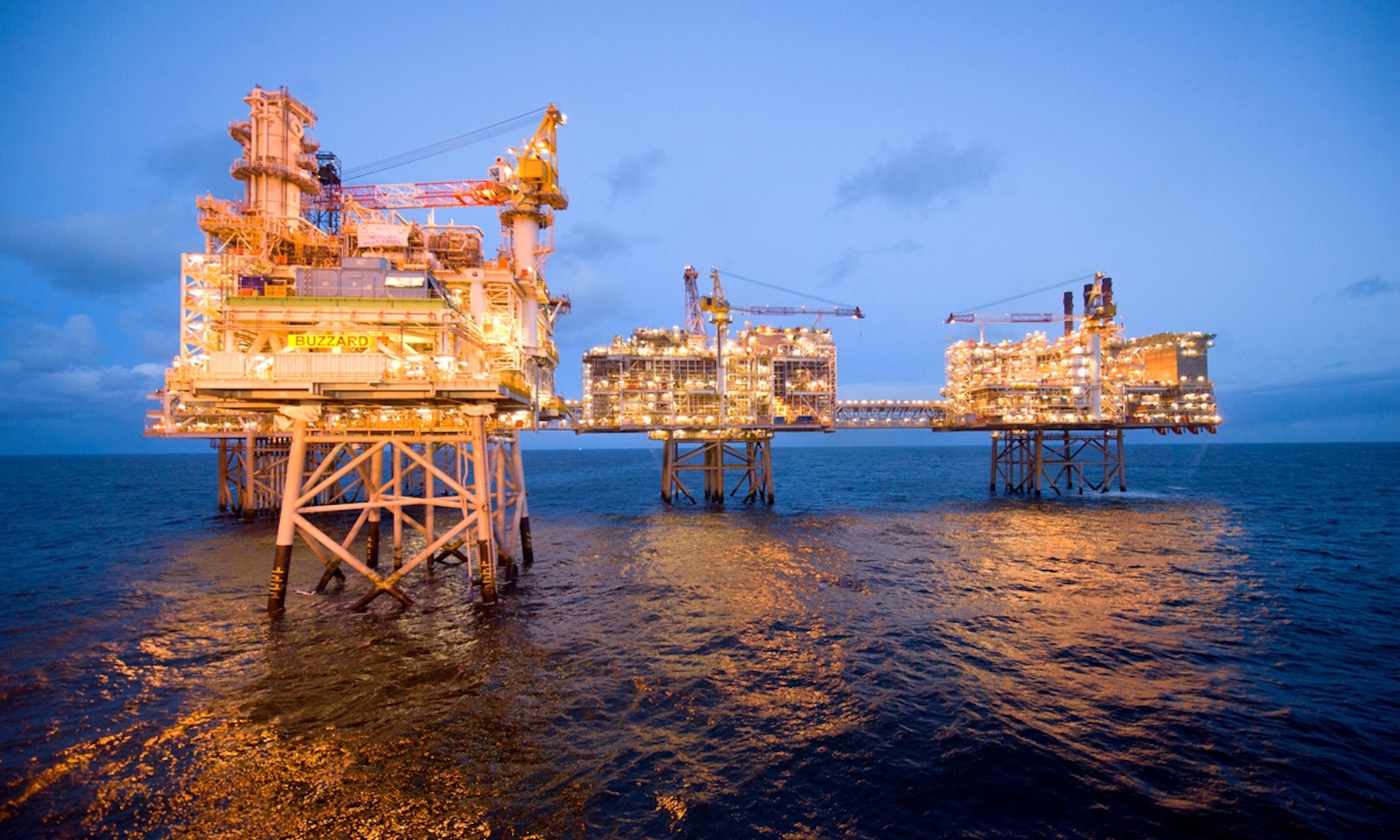
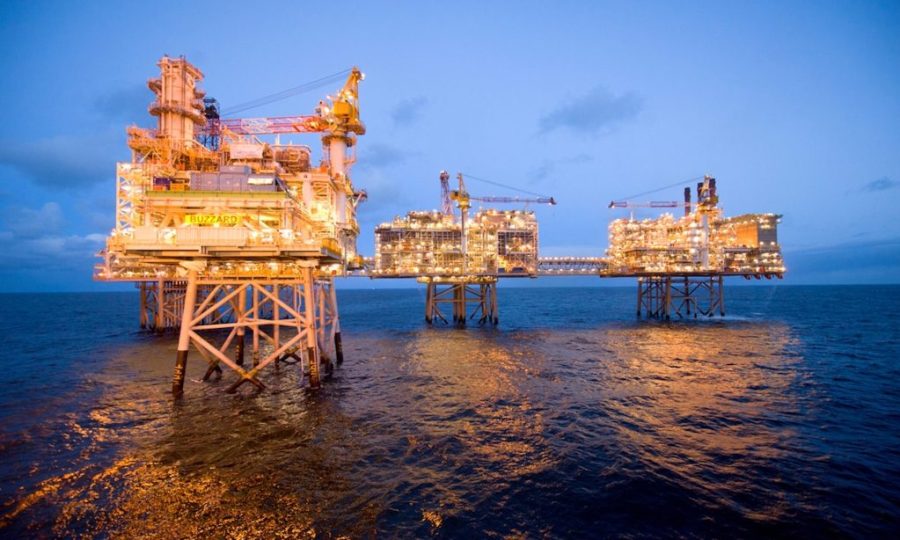
The China National Offshore Oil Corp (CNOOC) began production at Mero2, a deep-water pre-salt oil project in Brazil, on Tuesday, according to reports.
Located in Mero, the country’s third-largest pre-salt oilfield in the Santos Basin off southeastern Brazil, Mero2 is the second of four production units planned for the area. The Chinese state-owned company puts the production capacity of the project at 180,000 barrels of crude oil per day.
The Mero2 floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit was constructed and commissioned in China in June, arriving by ship in Brazil in September. Such units have become a staple of global offshore oil and gas development.
[See more: Petrobras welcomes new offshore oil platform to Brazil’s Mero field]
Mero1, the company’s first FPSO in the Santos Basin, came online in May 2022 and has a daily crude oil production capacity of 25,500 metric tons, making it one of the most productive offshore oil fields in Brazil so far.
Development of ultra-deep-water pre-salt oilfields like Mero has emerged as a significant trend in the global petroleum industry. Such fields account for one-third of the world’s petroleum reserves but drilling them is expensive. Each of the wells in Mero, for example, must extend at least 6,000 metres to pass through the deep water, post-salt sediments and salt layer before reaching the pre-salt oil.
Brazil’s pre-salt oil reserves, first explored by state-owned Petrobras in 2006, represent the biggest group of conventional oil discoveries this century and recent growth in oil output has been driven entirely by pre-salt production. CNOOC now owns and operates five pre-salt wells in the country.