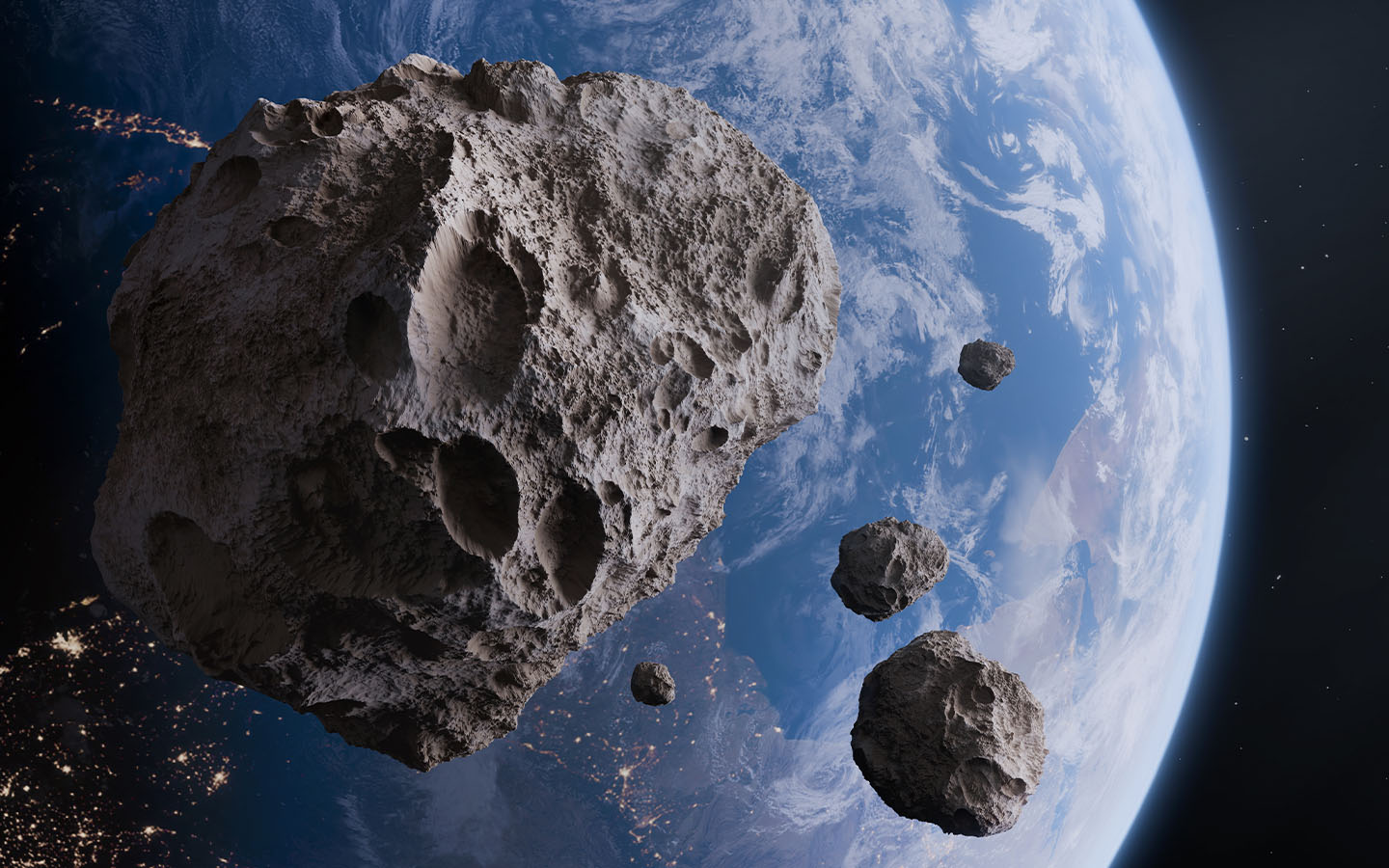
A large asteroid potentially headed towards earth has prompted China to assemble a planetary defence team, the South China Morning Post reports. The asteroid, named 2024 YR4, has a 2.2 percent chance of hitting earth in 2032, according to the European Space Agency (ESA).
The probability has surpassed the international monitoring threshold of 1 percent, activating asteroid response mechanisms around the world. In China, that led to new job openings at the State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defence, described as “planetary defence” posts.
The organisation is recruiting graduates to study ways of monitoring asteroids and to create early warning systems, the Post said – citing a notice posted last month on the WeChat account of the journal China Space Science and Technology.
[See more: China could win ‘the next industrial revolution,’ US congressional hearing told]
The US space agency, NASA, conducted the world’s first successful planetary defence test in 2022 and 2023, when it intentionally collided a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the asteroid moonlet Dimorphos – altering its orbital path (though Dimorphos did not pose any risk to the earth).
Estimated to be between 40 and 90 metres wide, 2024 YR4 is big enough to cause localised damage if it does collide with earth, according to NASA, which also noted that 2024 YR4’s impact probability could continue to rise. The asteroid, first observed last December, is currently at the top of ESA’s risk list.
The aerospace industry is a focus area for Beijing under its Made in China 2025 initiative. Recent accomplishments have included the publication of a high-definition moon atlas, based mainly on data compiled from Chinese lunar missions.